Dr. Priyanka Dorage
BAMS • MD (Ayurveda)
Assistant Professor at Maharashtra University of Health Sciences. Research author specializing in integrative Ayurveda and modern medicine. Published in multiple peer-reviewed journals.
Key Publication:
“Integrative Approach on Post-COVID-19 and Infertility: A Literature Review” (IJAM, 2023)
Becoming a parent is a dream for many couples. You track your cycle, follow ovulation, and even hear from your doctor that the egg was released. But then, pregnancy doesn’t happen.
It can feel confusing and heartbreaking, especially when everything seems normal.
The truth is, you’re not alone. This happens to many couples, and in many cases, it’s completely normal.
In this article, we’ll explain the possible reasons why conception doesn’t always occur and share the next steps you can take with hope and confidence.
If the egg ruptured, doesn’t that mean you should be pregnant?
Here’s the simple truth: When the egg is released, it only means your body is ready for a chance at pregnancy. But pregnancy doesn’t happen automatically. For conception to take place, healthy sperm need to meet the egg, your tubes must be clear, your uterus has to be ready, and your hormones must support the process. If even one step is missing, pregnancy may not occur.
Now let’s look at why this happens and the steps you can take.
Ovulation Confirmed but No Pregnancy: Sneha’s Real Story Explained
Sneha, a 30-year-old woman, had regular menstrual cycles. Every month, her ovulation was confirmed, so she expected pregnancy to happen soon. But even after trying for six months, nothing worked.
So, she decided to meet a doctor. After running some tests, the doctor found that her uterus was not ready to accept the fertilized egg. The reason was low progesterone levels after ovulation.
With hormone support, her body finally became ready. Soon after, she received the happiest news that she was pregnant.
If you are going through something similar, remember that you are not alone. In this article, we will explain the reasons this can happen and the steps that may help you.
What Happens After Egg Rupture But No Conception?
Ovulation sounds like the main event and it’s important but it’s only the start.
Here’s what needs to happen after the egg ruptures:
- The egg enters the fallopian tube
- It has 12–24 hours to meet sperm
- If fertilized, it takes 5–7 days to reach the uterus
- It must implant into a thick, healthy uterine lining
📍 Ovulation to Pregnancy — Understand Step by Step
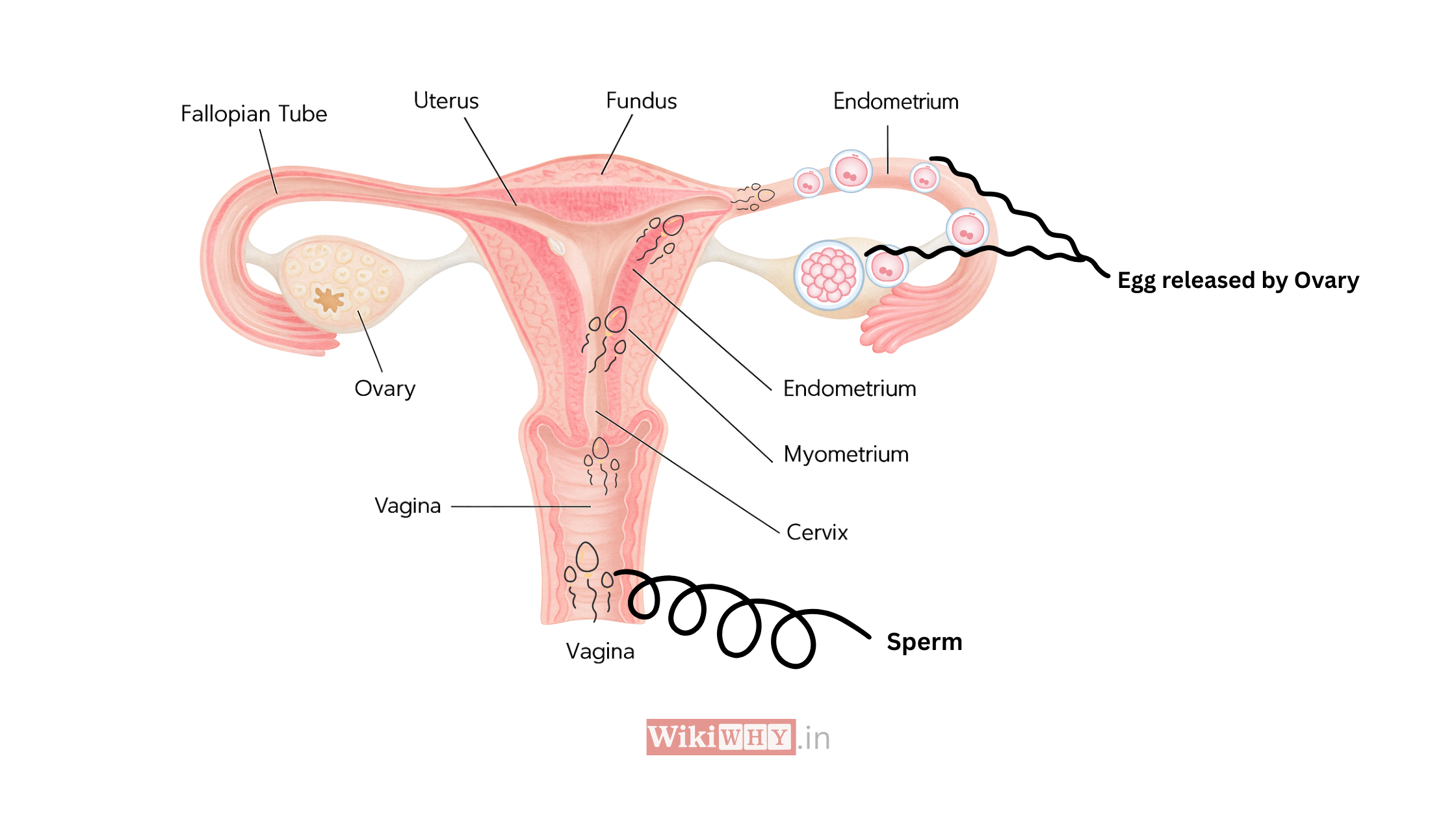
However, anything in this process is broken, pregnancy won’t occur.
10 Simple Reasons Pregnancy May Not Happen Even If You Ovulate
What Stops Pregnancy After Egg Rupture? With Data
These values are based on medical research and clinical experience from fertility specialists.
1. Sperm wasn’t strong enough
Sometimes the sperm does not reach the egg because it is not healthy enough. A low sperm count, slow movement, or an unusual shape can all make the journey difficult. Even when ovulation happens perfectly, pregnancy may not occur if the sperm cannot complete its job.
2. Timing Could Be the Issue
Fertility depends a lot on timing. Sperm can survive in the female body for up to five days, but the egg only lives for about 24 hours. If sex does not happen during this short fertile window, the egg and sperm may simply miss each other.
3. Fallopian Tubes Are Blocked
For sperm and egg to meet, the fallopian tubes must be clear. If they are blocked due to an old infection, inflammation, or surgery, fertilization cannot happen. Many women only discover blocked tubes when they consult a doctor for fertility issues.
4. The Endometrium isn’t Prepared
Even if the egg and sperm meet, the uterus also needs to be ready. If the lining is too thin, has growths like fibroids, or is swollen from inflammation, the embryo cannot attach properly. In short, the “nest” is not soft and safe enough for the baby to stay.
5. Low Progesterone (Luteal Phase Issue)
Progesterone is the hormone that prepares the uterus for pregnancy. It thickens and maintains the endometrial lining so that the embryo can implant securely. If progesterone levels are too low, the lining may not support implantation, or an early pregnancy may end before it fully establishes.
6. PCOS, or Hormonal Control Issues
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a common reason for infertility. Even if ovulation occurs, excess insulin, high prolactin, or thyroid imbalances can interfere with conception. Hormonal disruptions can make the environment unfavorable for fertilization or implantation., but steroid hormones such as insulin; prolactin; or thyroid could still work against you.
7. Egg Quality Is Low
Not every egg released during ovulation is healthy. As women age, especially after 35, egg quality tends to decline. If the egg has chromosomal abnormalities or is not genetically strong, fertilization may fail or the resulting embryo may not develop properly.
8. Cervical Mucus Issues
Cervical mucus plays a very important role in helping sperm travel smoothly toward the egg. If the mucus is too thick, too acidic, or hostile, sperm may struggle to survive or move forward. This barrier reduces the chances of successful fertilization.
9. Genetic or Chromosomal Issues
Sometimes, everything seems right—ovulation, sperm health, timing, and implantation. Yet, the embryo does not survive. In such cases, genetic or chromosomal abnormalities may be the reason. These issues are usually beyond anyone’s control and can happen naturally. It is not anyone’s fault
10. Stress
Stress plays a bigger role in fertility than many people realize. High stress triggers the release of cortisol, a hormone that disrupts reproductive hormones. This can affect ovulation, egg quality, and even implantation. In addition, lifestyle factors such as smoking, alcohol, poor diet, and lack of sleep can all reduce fertility.
Is This Normal? Or Should You Be Worried?
Yes, it’s normal to a point.
But you should consult a doctor if:
- You’re under 35 and trying for over 12 months
- You’re over 35 and trying for over 6 months
- You have irregular or painful periods
- You’ve had two or more miscarriages
Fertility Tests That Reveal What’s Happening
Doctors usually suggest:
- Blood tests: Check important hormones like FSH, LH, estrogen, progesterone, thyroid, and prolactin.
- Ultrasound scan: Tracks how the egg grows and confirms if it is released (ovulation).
- Semen test: Looks at the number of sperm, how well they move, and their shape.
- HSG (tube test): An X-ray test to see if the fallopian tubes are open or blocked.
- Endometrial biopsy: A small sample of the uterus lining is checked to see if it is healthy and ready for pregnancy.
Lifestyle Changes That Truly Help
Don’t ignore the basics—they really do matter. Small, regular and healthy habits can make a big difference for your fertility and overall health.
- Eat well: Choose fresh and colorful foods like berries, nuts, green vegetables, and fish. These give your body the right nutrients.
- Reduce caffeine and alcohol: Too much of these can affect your chances of conceiving.
- Stop smoking: Smoking harms fertility in both men and women, so stopping can really improve your chances.
- Sufficient Sleep: Aim for 7–8 hours of good sleep every night so your body can rest, repair, and stay balanced.
- Track your ovulation: Use an app, test strips, or even your body’s temperature to know the right time for conception.
- Care for your mental health: Stress can affect fertility too. Try walking, yoga, talking to a loved one, or enjoying a hobby to keep your mind calm and healthy.
Medical Interventions If Nothing Works
If it’s been months and nothing’s happening, don’t panic. These treatments can help:
- Ovulation-stimulating meds: Clomid or Letrozole
- IUI (Intrauterine Insemination): Sperm placed directly inside uterus
- IVF (In Vitro Fertilization): Egg and sperm joined in a lab
- Progesterone therapy: Thickens lining after ovulation
Another Real Story Of Riya
Her doctor suggested a saline ultrasound. It revealed a tiny polyp in her uterus—barely a few millimeters.
It was removed, and she conceived the very next month.
Sometimes, the smallest things make the biggest difference.
How It Feels: The Unseen Emotional Toll
When a cycle fails, it can break your spirit a little each time. The mix of frustration, confusion, and loneliness is real. And yet, many people keep silent about it.
But remember this, you’re allowed to feel upset. You’re allowed to cry or pause when it feels too much. And if your mental health is suffering, take the next step and reach out a fertility counselor or even a support group can make a huge difference.
Closing Statement: Take Back Control of Your Life
Not getting pregnant after ovulation does not mean something is wrong with you. It only means your body, which is wonderfully complex, may need a little extra support.
Fertility is not a race but it’s a journey. And no matter how you reach your goal—whether naturally, with a doctor’s help, or by slowly healing—you deserve love, care, and hope at every step.
Most importantly, remember this: you can do it, and you are never alone.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
Q1. Is it possible to ovulate but still not get pregnant?
Yes. Even if you release an egg during ovulation, pregnancy depends on many other factors, including healthy sperm, good timing, and a supportive uterus. That’s why ovulation alone doesn’t always guarantee pregnancy..
Q2. If my egg is released, does that mean I’m fertile?
Not always. Egg release (ovulation) is an important step, but pregnancy also depends on healthy sperm, open fallopian tubes, and a supportive uterus. All these need to work together for conception to happen..
Q3. Should I be worried if I haven’t conceived after 3 months of trying?
Not yet. Many couples take a few months before pregnancy happens. If you’ve been trying for 6 months or more without success, it’s a good idea to talk to a doctor for guidance.
Q4. Does age really reduce the chances of getting pregnant?
Yes, age does play a big role in fertility. As women age, especially after 35, the number and quality of eggs begin to decline. This can make it harder to conceive naturally. However, many women in their late 30s and even 40s still become pregnant with proper care, a healthy lifestyle, and timely medical support..
Q5. Can emotional stress alone stop conception?
Stress by itself usually does not make pregnancy impossible, but it can affect your chances. High levels of emotional stress may disrupt your hormones, delay ovulation, and reduce fertility. Staying relaxed and managing stress through healthy habits can improve your chances of conceiving naturally..