When you look up at the night sky, the stars shine like tiny lights far away. But if you watch closely, you will notice that stars do not shine continuously. Instead, they look like they are flickering or blinking. This makes many people wonder: why do stars twinkle?
The truth is, stars themselves do not really blink or change their light. What makes them twinkle is Earth’s atmosphere. The air around our planet is always moving, with layers of warm and cool air mixing together. When the light from a star travels through this moving air, it bends slightly in different directions. Because of this bending, the star’s light looks like it is shaking or flickering by the time it reaches our eyes.
That is why stars twinkle when we see them from Earth. But if you were in space, above the atmosphere, you would see stars shining steadily without any flicker. In this article, we will find out why stars twinkle in the night sky. We will explain the real reason for this blinking.
Why Do Stars Twinkle But Planets Do Not: Real Scientific Reasons
Stars do twinkle prominently, planets tend to emit a steady, unchanging light. Why is that?
The primary reason is apparent size. Stars are quite distant and thus appear as points of light, subject to the influences of atmospheric disturbances. Planets, while still distant, are closer in astronomic terms and display a disk when viewed with telescopes.
Due to their greater apparent size, the light from planets becomes smoothed out over a greater area, and they are less susceptible to the twinkling effect. Even planets, though, will appear to flicker when viewing conditions are extremely turbulent.
What Does It Mean When a Star Twinkles?
Twinkling means the way a star’s light looks like it is quickly changing in brightness or position when we see it from Earth. This makes stars look like they are flickering or shining unevenly in the night sky.
Sometimes the twinkling is so strong that a star may even seem to change colors from red to blue or white in just a few seconds. But this is not magic at all. It is science. The answer to why stars twinkle lies in how starlight travels through Earth’s moving atmosphere.
Scientific Explanation: Why Do Stars Twinkle?
Light Travel and Atmospheric Interference:
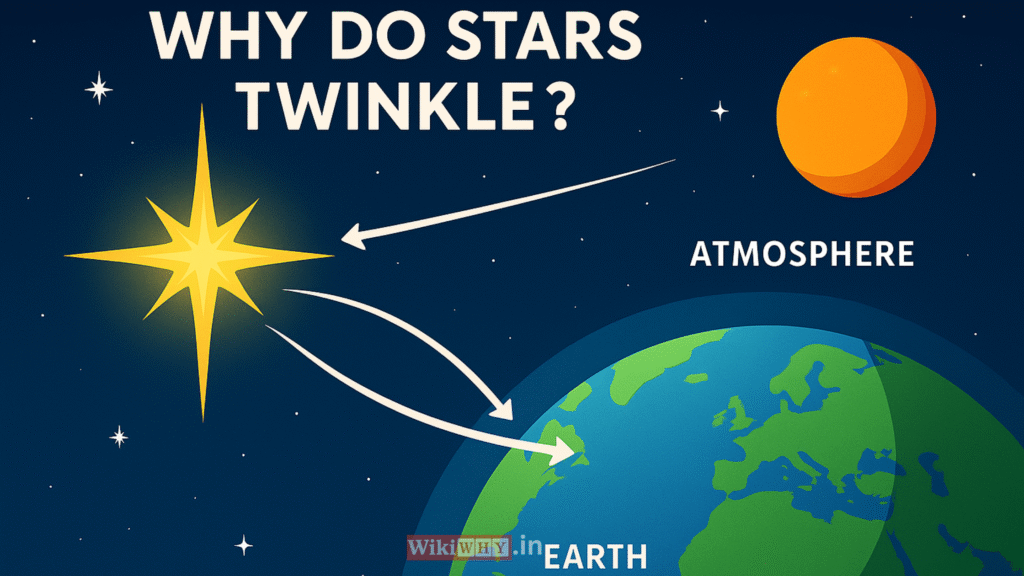
Stars are actually distant suns, and they shine from many trillions of miles away. Their light travels in a straight line through the emptiness of space without any disturbance. But once that light enters Earth’s atmosphere, things start to change.
Our atmosphere is made up of many layers of gases, and each layer has different temperatures and densities. Because of these differences, the light from stars bends, a process called refraction, again and again before it reaches our eyes.
This constant bending makes the starlight shift slightly in brightness and direction. As a result, when we look up at the night sky, the stars seem to flicker or twinkle.
The Role of Earth’s Atmosphere
The atmosphere of the Earth is a turbulent ocean of flowing air currents. When light from a star travels through this changing medium, it is refracted in various directions.
The cold and hot pockets of air make this refraction uneven, so the star seems to shift its position, magnitude, and even color instantly.
This is the reason why stars close to the horizon tend to twinkle more dramatically. Their light travels through a thicker slice of the atmosphere and meets more refraction and turbulence.
Astronomical Term: Stellar Scintillation
The technical term for the twinkling of stars is stellar scintillation. This term particularly describes the fluctuations in brightness and color produced by the atmospheric disturbance of starlight.
Professional astronomers also consider stellar scintillation for their observations and utilize technologies to reduce its influence, particularly for telescopes based on the ground.
Do All Stars Twinkle?
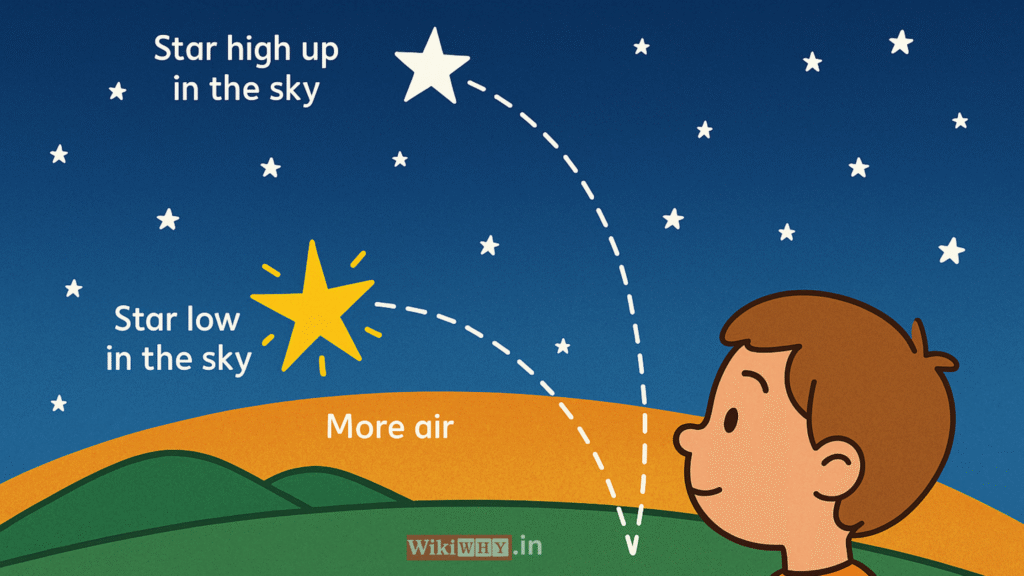
Stars that appear lower in the sky (close to the ground) have their light travel through more atmosphere than those directly overhead. This makes them more prone to distortion and twinkling.
Meanwhile, stars overhead pass through less atmospheric interference, so they stay steadier and twinkle less than those near the horizon.
Can We Observe Twinkling Stars From Space?
Surprisingly, the twinkling of stars is a terrestrial phenomenon. Astronauts on board the International Space Station (ISS) and other spacecraft observe stars as steady, unblinking blobs of light.
This is because in space there is no atmosphere to deflect or disperse the light. Without Earth’s atmosphere interfering, the stars twinkle with a consistent radiance. A sight astronomers attempt to simulate using space-based observatories such as Hubble and the James Webb Space Telescope.
- Twinkle Twinkle Little Star Facts Twinkle Twinkle Little Star is more than just a nursery rhyme. it’s a reflection of real science!
- Some stars twinkle in other colors because of atmospheric dispersion.
- Twinkling is more pronounced during winter because of greater atmospheric instability.
- Airplane lights and satellites do not twinkle; this makes them easy to identify as not being stars.
- Adaptive optics used in contemporary telescopes assist in removing the twinkling effect.
How Twinkling Impacts Astronomy
Twinkling of stars presents difficulties for astronomers. Ground-based telescopes are affected by decreased picture clarity because of the interference of the atmosphere.
To combat the same: Telescopes are constructed at high elevations (such as in Chile or Hawaii) where the atmosphere is thinner and more constant.
Adaptive optics equipment compensates in real time for atmospheric turbulence by adjusting the telescope’s mirrors.
Space telescopes such as Hubble are positioned outside Earth’s atmosphere, providing crystal-clear views of stars and galaxies.
The Mystery Behind Twinkling Stars Unraveled
- So, why do stars twinkle? It all boils down to Earth’s atmosphere. As the light from distant stars travels across space and enters our atmosphere, it gets distorted by layers of air with different temperatures and densities. This causes the light to bend and shift, making the stars appear to flicker and shine in varying colors.
- Though it’s a seemingly harmless oddity, stellar twinkling is a critical aspect of astronomy, assisting researchers in developing improved equipment and selecting ideal vantage points.
- The next time you look up and see a star twinkling, keep in mind — you’re not merely gazing upon a beautiful glow. You’re seeing a stellar show influenced by Earth’s atmosphere and the enormity of space.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why do stars twinkle but planets do not?
Stars are so far away that they look like tiny points of light. Their light is disturbed by Earth’s atmosphere, making them appear to twinkle. Planets look bigger in the sky, so the effect gets averaged out and they appear steady.
Why do stars twinkle more near the horizon?
When stars are low in the sky, their light has to pass through more air and turbulence, which bends the light more. This makes the twinkling stronger near the horizon.
Can stars twinkle in different colors?
Yes. The atmosphere can split the star’s light into different colors for a moment, so you might see a star quickly shift between red, blue, and green.
Do stars twinkle when viewed from space?
No. Astronauts in space or telescopes like Hubble see stars without twinkling because there is no atmosphere to disturb the light.
Why do planets sometimes seem to shine brighter than stars?
Planets are closer to Earth and reflect sunlight, so they often look brighter and steadier than stars, even though stars are much bigger.
Which planets are easiest to see without twinkling?
Venus, Jupiter, and Mars are the easiest to spot with the naked eye. They shine steadily, unlike stars, which helps people tell them apart.